 IST/ISR participated in the 1996 edition of
the Festival des Sciences et
Technologies , held annually at La Ferté Bernard, France.
Three IST final year undergraduate students (Pedro Aparício, Pedro
Raposo and João Ferreira) carried out the development work.
The team was supervised by IST Professors
Pedro Lima and
Carlos Cardeira.
IST/ISR participated in the 1996 edition of
the Festival des Sciences et
Technologies , held annually at La Ferté Bernard, France.
Three IST final year undergraduate students (Pedro Aparício, Pedro
Raposo and João Ferreira) carried out the development work.
The team was supervised by IST Professors
Pedro Lima and
Carlos Cardeira.
The project was supported by JNICT, several Portuguese private and public companies, and the French Embassy.
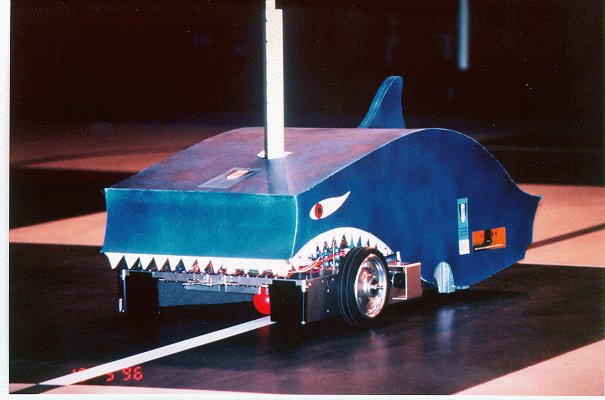
BARBANETA is a differential drive vehicle aimed at following an optical track (40Kb) in the absence of heavy obstacles, but modularly designed to allow future conversion into an autonomous mobile platform. The system uses 16 infrared (IR) sensors (88Kb) - similar to those used by the Beirute AGV - to follow a floor-painted track, and an optical RAM to detect and recover from a track interruption by searching and moving towards a passive beacon. It can also collect and discriminate (51Kb) billiard balls of three different colors (black, white and red) scattered along the track. The mechanical design was conceived by the students and implemented by Mr. Luis Raposeiro, a technician from IST Mechanical Engineering Department. A bottom view (37Kb) of the vehicle shows the two RS DC motors used and the alternative paths for the billard balls, as well as the discrimination system for the billiard balls, based on a step motor.
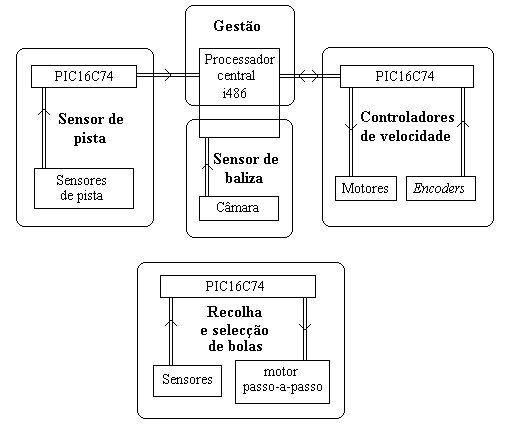
The relation between the functional and hardware architectures can be understood from the following diagram (it is in Portuguese, but you can surely understand it!):

|
|
|
|
|
|